Ethereum Layer-2 Blockchains: What are They and Key Benefits

Ethereum, the second most popular blockchain network trailing behind Bitcoin, faces similar scalability challenges, managing a maximum of 40 transactions per second (TPS) compared to the over 60,000 TPS capacity of payment giants like VISA and Mastercard.
To address this bottleneck and reduce transaction fees, Vitalik Buterin and the Ethereum Foundation are exploring ways to enhance the network’s TPS. Meanwhile, third-party developers are taking matters into their own hands by implementing Ethereum Layer 2 solutions.
Let’s look closer at what is Layer 2 Ethereum and how to use Layer 2 on Ethereum ecosystem.
Understanding Layer 2 Solutions
Consider a scenario where you and your neighbor decide to streamline your transactions, such as buying and selling goods, by recording them on paper and settling in cash monthly instead of daily.
This analogy mirrors the relationship between Ethereum’s main blockchain (Layer 1) and Ethereum Layer 2 solutions (L2). Layer 2 operates atop Ethereum, running parallel operations that enhance transaction capacity and speed by offloading some of the work from the main chain.
Layer 2 solutions allow users to conduct transactions within their network, then batching and updating those on the main Ethereum blockchain by a smart contract. This process speeds up transactions. It also maintains security by leveraging Ethereum’s robust network to verify the accuracy of Layer 2 transactions.
The key steps include transaction submission by users, validation by L2 nodes, batching by a sequencer node, and finally, the publication of these transactions on Ethereum by a proposer node.
L2 solutions might even have different architecture and virtual machines compared to L1. E.g. Ethereum L2 Metis utilizes Solana Virtual Machine instead of EVM. Still, L2s are connected with L1 by a smart contract that sources L2 state updates on L1 to make L2s more secure.
Typically, Layer 2 operates as follows:
- L2 users submit transactions.
- L2 validator nodes validate and execute transactions.
- L2 sequencer node batches the transactions and updates the whole network state.
- L2 proposer node publishes the updated state and some transactions’ details on L1.
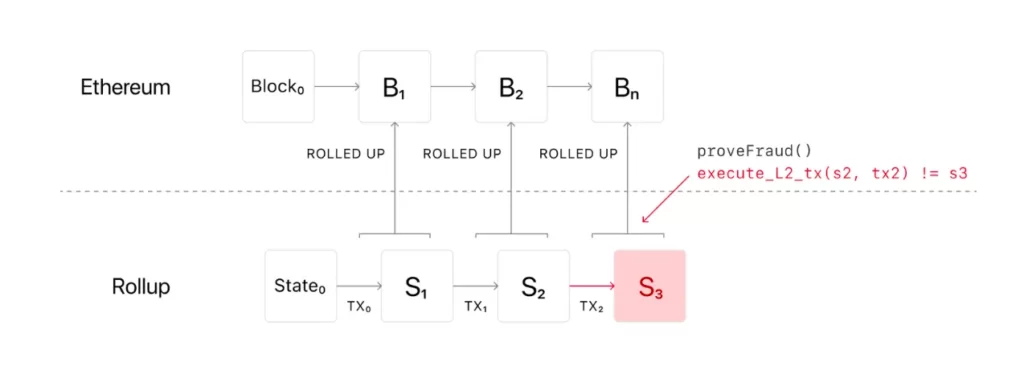
The reason for storing transaction data on L1 is to be sure that the L2 transaction history matches the latest state. This eliminates the threat of a bad actor pushing invalid transactions on L2. The whole transaction history is stored on a secure L1 and those illicit transactions could be spotted, disputed, and reverted.
How Do L2s Enhance Ethereum’s Scalability?
Layer 2 networks streamline the consensus process with a smaller group of validators, enabling quicker agreement. This efficiency allows developers to significantly reduce the time it takes to create a block. This goes from the standard 10–12 seconds on Ethereum to as little as 1 second or even 500 milliseconds.
The acceleration can increase the number of transactions processed per second by a factor of ten compared to Ethereum. Additionally, by expanding the block gas limit, one can include more transactions in a single block, further boosting the transactions per second (TPS) rate.
With the rise in TPS, transaction fees begin to drop due to the elimination of fee competition. Provided the transaction fees suffice to cover Layer 2’s operational costs (the base fee plus the cost of publishing on Ethereum, divided by the number of transactions in a batch), transactions are executed promptly and efficiently.
While fees can’t drop to zero — since the network incurs costs in ETH to update its state on the costly Ethereum network — the spread of these Ethereum fees across all users in a batch significantly reduces the cost burden on individual Layer 2 transactions.
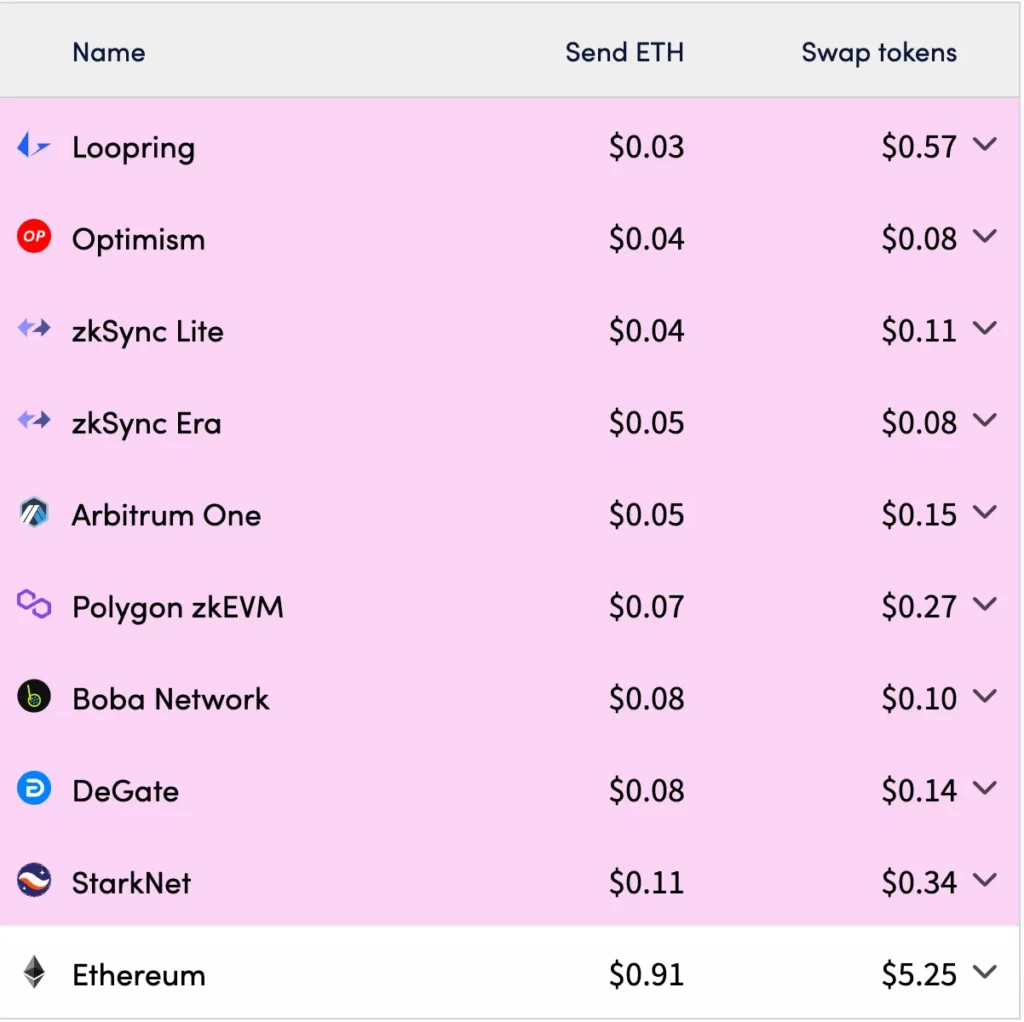
Ethereum layer 2 projects development often uses the same EVM as Ethereum (L1) to achieve full compatibility with it. The developers can easily migrate their projects from Ethereum to L2, offering users a version that is both faster and more cost-effective. Moreover, Layer 2 teams consistently implement bridges to facilitate easy asset transfers between Ethereum and Layer 2 platforms, enhancing the multi-chain user experience.
Overall, Layer 2 scaling solutions on Ethereum provide a trifecta of benefits. They are reduced fees, quicker transaction processing, and access to the familiar tools and languages, such as Solidity and MetaMask, that the Ethereum community has grown to rely on.
Why Aren’t Ethereum Layer 2 solutions Completely Secure?
Vitalik Buterin introduced the concept known as the blockchain trilemma, which posits that a blockchain network cannot simultaneously excel at scalability, security, and decentralization. Invariably, one of these aspects suffers. For instance, XRP achieves speed and security at the cost of centralization. Meanwhile, Bitcoin and Ethereum maintain security and decentralization but at the expense of performance and higher fees.
When it comes to Layer 2 solutions for Ethereum, they offer scalability and a degree of decentralization. Yet, they face challenges in security due to potential single points of failure, such as sequencer and proposer nodes. These critical components are usually managed by the teams behind L2 solutions, requiring users to place their trust in these entities.
Should a sequencer node malfunction or be compromised, users are forced to revert to manual transactions on the main Ethereum network (Layer 1) or wait till devs fix it. In some cases, if the sequencer node goes down, it can halt the entire network. Similarly, a malfunction in the proposer node can prevent users from withdrawing their funds to Layer 1. Moreover, issues with the data availability layer could result in transaction reversals or losses.
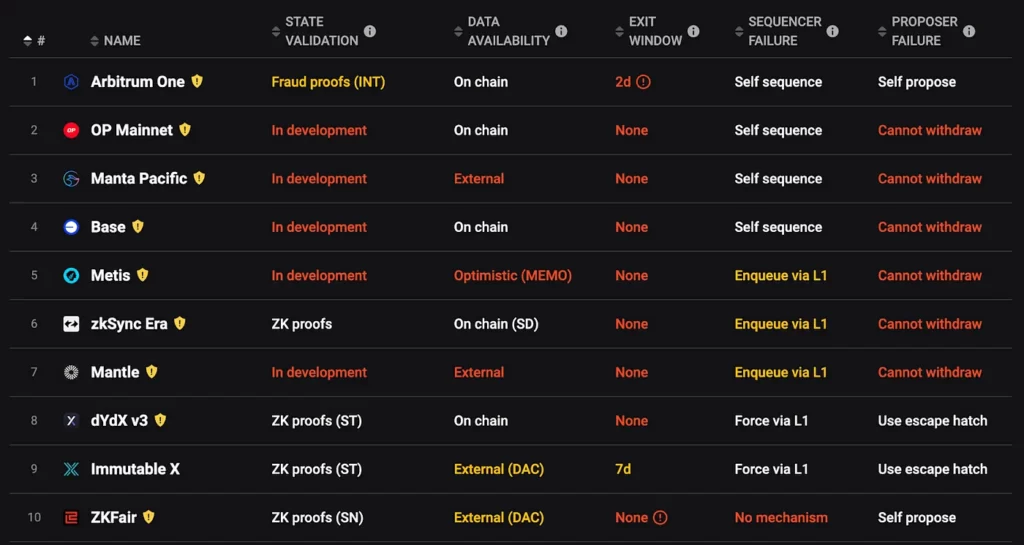
The sequencer and proposer failures are a real threat. Arbitrum’s sequencer failed once because it ran out of ETH to pay L1 fees. ZkSync network halted for a time because of sequencer overload. Single point of failure as it is.
Another concern is the use of off-chain storage for transaction data by some Ethereum Layer 2 scaling solutions. If this data is ever compromised or lost, it leaves no recourse to confirm those transactions occurred.
Additionally, the security of bridges between Layer 1 and Layer 2 networks is a significant concern. Out of $5.8 billion lost in DeFi hacks $2.8 billion were lost due to bridge hacks. This vulnerability further emphasizes the complex security landscape facing Ethereum Layer 2 tokens.
Exploring Layer 2 Technologies
The Layer 2 concept is simple: spin up a network, execute transactions, and post state updates on L1. There are four main ways to implement this strategy: using an optimistic approach or ZK-proofs.
Optimistic Rollups
Optimistic Rollups are foundational Layer 2 solutions that operate on the principle of optimism. This means they proceed under the assumption that all transactions batched for Layer 1 are legitimate and mirror those on Layer 2. Validators later review these transactions and can challenge their validity by presenting fraud proofs. If someone tampers with the transactions, the network rolls back to solve the problem.
Pros: They require less computational power to run a node.
Cons: Withdrawals back to Layer 1 can take up to seven days as nodes undergo a cooldown period for submitting any necessary fraud proofs.
Leading examples of Optimistic Rollups include Optimism, Arbitrum One, and Boba Network.
ZK Rollups
ZK Rollups take a different approach by utilizing validity proofs rather than assuming the best. Each transaction batch published on Layer 1 is accompanied by a ZK-proof, which verifies the accuracy of the batch’s computational outcome. While more secure, this method is resource-intensive due to the gas required to generate ZK-proofs.
Pros: Withdrawals are instantaneous, with no need for a cooldown period.
Cons: The high computational and financial costs associated with generating ZK-proofs.
Prominent ZK Rollups include zkSync Era, Starknet, and Polygon zkEVM.
Validiums
Validiums are a lighter version of ZK Rollups, choosing not to publish transaction data on Layer 1 and instead only posting ZK-proofs. The transaction data is stored entirely off-chain, making the availability of this data critical for the system’s operation. To mitigate risks, Validiums utilize Data Availability Committees (DAC) to ensure transaction details are always accessible.
Pros: They are faster and more cost-effective than ZK Rollups, with no withdrawal cooldown.
Cons: Storing data off-chain introduces potential security vulnerabilities.
Well-known Validiums include Immutable X, StarkEx, and zkPorter.
Optimiums
Optimiums are among the rarest Layer 2 solutions, merging the off-chain data storage feature of Validiums with the fraud-proof mechanisms of Optimistic Rollups. They update only the state on Layer 1 while keeping transaction data off-chain. Without ZK-proofs, transactions are considered “pending” on Layer 1 for a week. It allows time for validators to issue challenges or request fraud proofs from DA operators.
Pros: They offer a more cost-effective and faster alternative to other Layer 2 technologies.
Cons: The reliance on off-chain data storage and a 7-day withdrawal cooldown mirror the challenges faced by Optimistic Rollups.
Each of these Layer 2 technologies offers unique advantages and challenges, contributing to the future and ongoing evolution of Ethereum’s scalability and efficiency.
Should You Launch Your Project on a Layer 2?
Considering launching your project on an L2 network? Layer 2 protocols on Ethereum launches can be a game-changer if your project involves constant user interaction, such as a decentralized perpetual trading protocol, a wallet, a Web3 game, or a prediction market.
The reduced fees and increased speed offered by L2s can significantly enhance user experience. Many white-label web3 solutions work on L2s. Some projects even develop their own L2 solutions, known as app chains, designed specifically to meet the unique requirements of their project. Additionally, emerging Layer 2 Ethereum coins may offer liquidity and less competition compared to traditional tokens, presenting an opportunity for your project to capture a new audience.
Read more about What Are Layer 2 Networks here.
Consider if the difference between a transaction settling in a minute versus a second is negligible to your users, or if they are indifferent to higher transaction fees. Then, sticking with an L1 solution might be the better choice. The Ethereum-based network, for example, provides unparalleled security and liquidity. Yet, it’s important to note that you’ll be in direct competition with heavyweights like Uniswap and Opensea.
It’s worth mentioning that most L2s are compatible with the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) with only slight modifications, making it feasible to launch your project on Ethereum with later migration to an L2 or the other way around. Numerous decentralized exchanges have already leveraged this flexibility.
Want to read more about Ethereum in our blog? Take a look at this Ethereum Restaking post.


