Runes Over Ordinals: The Next Generation of Bitcoin Tokenization

Bitcoin has long been associated primarily with its role as a store of value and medium of exchange. However, the advent of new protocols like Ordinals and Runes reshapes this narrative, introducing the concept of fungible and non-fungible tokens to the Bitcoin blockchain.
This guide provides a closer look at the Bitcoin Runes protocol to cover its benefits, technical aspects, use cases, and how it compares to the BRC-20 token standard. Aimed at CEOs, CFOs, CIOs, as well as crypto enthusiasts, this comprehensive overview will help you understand and use Runes effectively.
What are Bitcoin Runes?
Runes is a new type of fungible token on the Bitcoin blockchain, introduced in September 2023 by the creator of Ordinals, and launched on the 20th of April — the day of the fourth halving. They were designed as a response to the criticism of BRC-20 tokens, aiming to be more efficient and less “spammy” while still allowing for easy creation and management of fungible tokens on Bitcoin.
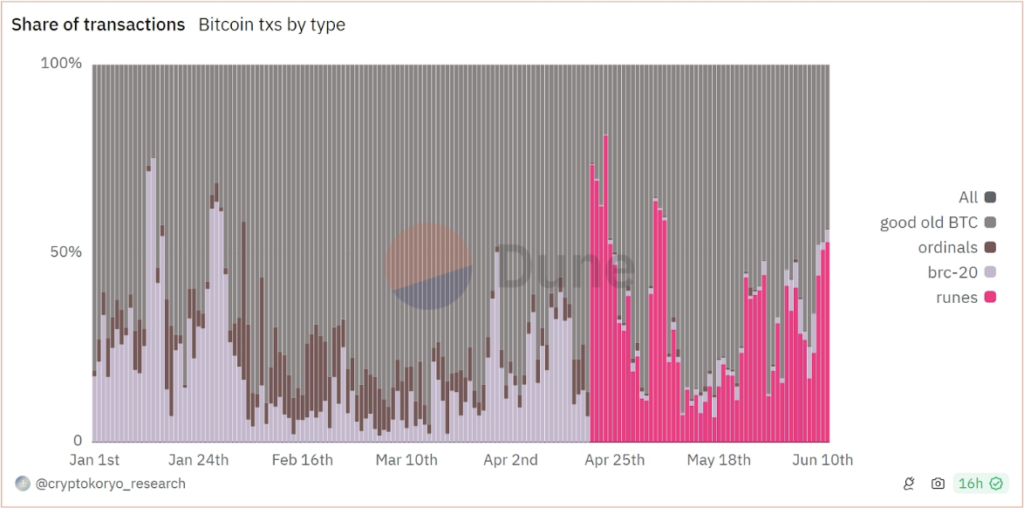
Runes drove innovation in Bitcoin. “Rune” share in transactions in April 2024 reached 81.3%, raising fees to $128.45. Hype faded and the fee went to $4.66. Total “rune” transactions: 12.2M. These tokens boosted Bitcoin’s robust infrastructure by using the UTXO (Unspent Transaction Output) model and the OP_RETURN opcode to embed arbitrary data within Bitcoin transactions.
In simple words, Ordinals function similarly to NFTs based on ERC-721 token standard, for instance, serving as unique digital assets. BRC-20 tokens resemble ERC-20 tokens, allowing for the creation and trading of custom tokens on the Bitcoin network. Meanwhile, Runes is a protocol that aims to improve the functionality of BRC-20 tokens.
Ordinals: Bitcoin NFT Explained
Ordinals are a way to create Bitcoin NFTs by attaching data (like images and videos) to individual satoshis on the Bitcoin blockchain.
Introduced by Casey Rodarmor on January 20, 2023, Ordinals differ from earlier Bitcoin NFTs by not relying on separate layers or protocols. Instead, they use ordinal theory, which assigns a unique number to each satoshi, making them native to Bitcoin.
Since their launch, over 200,000 Ordinals have been minted, embedding various types of media into individual satoshis. Bitcoin NFTs use the SegWit (2017) and Taproot (2021) updates, which expanded the capacity of the first cryptocurrency to store arbitrary data. This allows for up to 4MB of data to be included in a transaction.
Ordinals use a system for ordering sats, giving each satoshi a unique ID, and the data attached to a satoshi is called an inscription. This process is backward compatible with Bitcoin and does not require any changes to the Bitcoin protocol.
Unlike Ethereum NFTs, which are distinguished by token IDs, Ordinals can be treated as either fungible or non-fungible, depending on the owner’s recognition of the ordinal data. This flexibility is unique to the Bitcoin protocol.
The introduction of Ordinals has sparked debate within the Bitcoin community about the blockchain’s primary use, balancing between financial transactions and new cultural or memetic values brought by NFTs.
The problem of Ordinals is that such sort of transactions are congesting the Bitcoin network, leading to higher transaction fees. Consequently, regular users must pay increased fees for their Bitcoin transactions.
On one hand, miners are benefiting from higher fees and rewards. On the other hand, some people are calling it a scam, while others are just along for the ride.
Inside the BRC-20 Protocol
BRC-20, inspired by Ethereum’s ERC-20 protocol, is a token standard created by an anonymous developer named Domo. Enabled by Bitcoin’s Taproot upgrade and the concept of Ordinals, BRC-20 tokens use script files on the Bitcoin blockchain to attribute tokens to individual satoshis (the smallest unit of Bitcoin), allowing JSON data embedding for deployment, minting, and transfers.
Before BRC-20, additional data in Bitcoin transactions was typically added with the OP_RETURN command, which allowed up to 80 bytes of metadata in an unspendable output. In contrast, BRC-20’s Ordinal approach embeds metadata within the transaction itself. The 2021 SegWit update increased storage for witness data beyond the 1MB block limit, and taproot script-path spend scripts offer up to 4MB for inscription content.
Sending a BRC-20 transaction involves two steps: committing a Taproot-enabled output to a script with the inscription content and revealing this content in a subsequent transaction. Larger content is split across multiple satoshis.
Special wallets, like ordinal and unisat wallets, are needed to maintain the correct order of satoshis, as regular wallets could lose the inscription data. The serial number and data are inserted into the witness signature field of transactions to ensure ownership and prevent double spending. Though experimental and not officially recognized, BRC-20 leverages Bitcoin’s security and simplicity for token transactions.
How Bitcoin Runes Work
Runes are aimed to simplify the creation and management of fungible tokens on Bitcoin, especially for meme coins and speculative assets. The protocol is described as simple, efficient, and secure, positioning it as a competitor to Taproot Assets and RGB.
To understand Runes, it’s essential to grasp two key concepts:
- UTXO (Unspent Transaction Output) Model: This system is fundamental to Bitcoin network transactions. It tracks unspent cryptocurrency balances available for future transactions. Each UTXO represents funds that can be spent in new transactions, ensuring transaction security by preventing double spending.
- OP_RETURN Opcode. The OP_RETURN opcode allows for the inclusion of non-financial data in Bitcoin transactions. Runes uses this opcode to inscribe data onto satoshis, effectively creating tokens via etching, minting, and edict.
Etching creates new Rune tokens on Bitcoin, defining their name, supply, etc. Minting produces these tokens after etching, either openly or under conditions. Edict sets transfer rules post-creation. These tools offer flexibility for token creation and management on Bitcoin.
Each UTXO can contain multiple Runes. The OP_RETURN field in a Bitcoin transaction stores Runestone messages, which are used to create and transfer tokens on the Bitcoin network.
A single Runes transaction can reference multiple operations across different “runes.” When a token is sent, Runes splits the transaction’s UTXO into several new UTXOs based on the instructions in the OP_RETURN data. Each new UTXO represents different amounts of tokens, which are then sent to recipients. If a transaction fails due to incorrect protocol messages, the runes are destroyed to prevent the creation of additional objects.
Using OP_RETURN, users can perform several operations:
- Etching — it involves creating an asset and registering its basic parameters, such as name, ticker, supply, and divisibility. During this process, issuers can also premine some runes for themselves before making them available to the public.
- Minting — after etching, a certain number of Runes can be generated through open or closed minting. Open minting allows anyone to create runes, producing a fixed number of new assets. Closed minting creates new tokens only under specific conditions, such as after a set period.
- Edict — the function sets rules for transferring Runes after etching or minting. It allows for batch transfers, airdrops, or moving all issued runes to a single account.
Benefits of Bitcoin Runes
Runes enables the creation of tokens for DAOs, gaming assets, and meme tokens on the Bitcoin blockchain, simplifying the process for developers and attracting new talent. They expand Bitcoin’s capabilities beyond its initial use case. Runes offer several key advantages on the Bitcoin blockchain.
- Efficiency. Runes utilize the OP_RETURN model, preventing unspendable UTXOs and using only 80 bytes of data compared to BRC-20’s 4MB, reducing network load and congestion.
- Simplicity. Runes enable straightforward creation and management of multiple fungible tokens on-chain, without off-chain data or native tokens, avoiding excessive “junk” UTXOs.
- Potential to expand user base. Runes, like Ordinals and BRC-20 before them, have sparked interest in meme coins and other tokens on Bitcoin, attracting new users and potentially expanding the Bitcoin’s ecosystem.
These advantages make Bitcoin Runes a promising new tool for creating and managing fungible tokens on the Bitcoin blockchain, with the potential to increase efficiency, simplify token management, and attract new users.
Use Cases of Bitcoin Runes

Runes are created on Bitcoin, but special wallets like Xverse and UniSat are needed to manage them. Marketplaces such as OKX and Magic Eden support Runes that allows users to list and trade them. Services like Luminex provide additional tools to track new collections and learn how to create Bitcoin Runes, mint, and transfer Runes.
DeFi. Runes can be used to create DEXs, lending platforms, and other DeFi applications on the Bitcoin blockchain. The emergence of the first Runes DEX is a testament to this potential.
Another real-world example of using Runes to create DeFi applications is the ALEX exchange. It is the first platform on Bitcoin, allowing users to trade Runes and BRC-20 tokens without intermediaries. ALEX utilizes the Ordinals protocol for inscriptions and Runes to create liquidity and facilitate trading of various tokens on the Bitcoin blockchain.
For instance, Gamma allows users to tokenize RWAs like art, music, or real estate using Bitcoin Runes on Bitcoin and the Ordinals protocol. This enables fractional ownership and increased liquidity for these assets, opening up new opportunities in the digital asset market.
Loyalty Programs and Rewards. Businesses can choose Bitcoin Runes to create loyalty programs, offering customers rewards in the form of tokens.
While no widely known examples exist yet, Runes has the potential for loyalty programs. Imagine a coffee shop issuing Runes for purchases, redeemable for discounts. This illustrates how Runes could transform rewards by offering a secure, transparent, and easily transferable alternative.
Options for Investing in Bitcoin Runes
First, it matters to say about the opportunities of investing in Bitcoin Runes for you to clarify the need to spend time and funds on it. So, let’s glimpse the 3 main cases to pay attention to this technology.
- Buying Runes. You can buy existing Runes on cryptocurrency exchanges that support them. Binance is one of the major exchanges that has listed several Rune tokens, but, as was previously mentioned, you have a vast choice.
- Creating Runes. If you have a project or idea, you can create your Runes by inscribing data onto satoshis. This process involves minting tokens and embedding the necessary metadata within Bitcoin transactions.
- Building Runes Infrastructure. Developers and entrepreneurs can contribute to the ecosystem to build and create Bitcoin Runes marketplace, wallets, and other tools. The cost of developing such platforms can vary depending on their complexity and features.
The next stop is the instruments for making your Runes fortune-telling easier without using tarot or dancing around the issue. The Runes ecosystem is growing fast, with both new and established venues adopting Rune technology.
These platforms can create assets on Bitcoin or offer tools for managing Runes. The main components of this evolving system include various tokens, launchpads, marketplaces, DEXs, wallets, and analytics webs.
- Rune Alpha. Etching, transferring, and market options are included.
- RunesTerminal with its 4 main products — RunesScan explorer, RunesPad free market, RunesEtch platform for issuing and sending new runes to individuals or in batches, and RunesBook Wiki.
- RuneMine with Portfolio, Multisig for managing and storing Runes, Bridge for cross-chain interactions, and The RuneMine Decentralized Indexer network overviewing all historical data.
Conclusion
Bitcoin’s evolution with Ordinals, Runes, and BRC-20 tokens showcases the dynamic nature of the blockchain ecosystem, each bringing unique benefits and use cases.
Ordinals offer a novel way to create NFTs while BRC-20 tokens, inspired by Ethereum’s ERC-20 protocol, facilitate the deployment, minting, and transfer of custom tokens on the Bitcoin network.
Runes is another spin of network evolution that simplifies the creation and management of fungible tokens on Bitcoin, particularly suited for meme coins and speculative assets.
These advancements underscore the importance of exploring new technologies and protocols. Experimenting with Ordinals, Runes, and BRC-20 tokens not only broadens our understanding of Bitcoin’s potential but also drives innovation and attracts new talent and users to the ecosystem.
The Dexola team is committed to staying ahead of the curve, providing our clients and community with the latest tools and insights in the cryptocurrency world.